With the rapid development of high frequency and high speed of electronic devices and integrated circuit technology, the total power density of electronic components increases substantially while the physical size is getting smaller and smaller, and the heat flux also increases. Therefore, the high temperature environment is bound to affect the performance of electronic components, which requires more efficient thermal control. How to solve the problem of heat dissipation of electronic components is the key point at this stage. Therefore, the heat dissipation method of electronic components is simply analyzed in this paper.
The efficient heat dissipation of electronic components is influenced by the principles of heat transfer and fluid dynamics. The heat dissipation of electrical devices is to control the operating temperature of electronic equipment, so as to ensure the temperature and safety of its work. It mainly involves the different contents of heat dissipation, materials and other aspects. At the present stage, the main heat dissipation methods are natural, forced, liquid, refrigeration, dredging, heat pipe and so on.
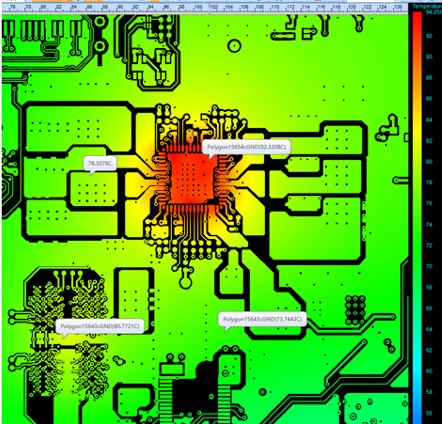
1, Natural heat dissipation or cooling mode Natural heat dissipation or cooling mode is under the natural condition, does not accept the influence of any external auxiliary energy, through the local heating device to the surrounding environment heat dissipation way for temperature control, the main way is heat conduction, convection and radiation concentration, and the main application is convection and natural convection several ways. The natural heat dissipation and cooling mode is mainly used in the electronic components with low temperature control requirements, and the equipment and components with low power consumption and relatively low heat flux of device heating. This method can also be used in sealed and densely assembled devices where other cooling techniques are not required. In some cases, when the heat dissipation capacity is relatively low, the characteristics of the electronic devices will be used to appropriately increase the influence of heat sink and heat conduction or radiation, and optimize the natural convection by optimizing the structure, so as to enhance the heat dissipation capacity of the system.

2,Forced heat dissipation or cooling method Forced heat dissipation or cooling method is a way to accelerate the air flow around electronic components by means of fans and take away heat. This method is relatively simple and convenient, and the application effect is remarkable. This method can be used in electronic components if the space is large enough to allow air flow or to install some cooling facilities. In practice, the main ways to improve such convective heat transfer capacity are as follows: to appropriately increase the total area of heat dissipation, relatively large convective heat transfer coefficient should be generated on the heat dissipation surface. In practice, increasing the surface area of the radiator is widely used. In engineering, the main way is to expand the surface area of the radiator by fin, and then strengthen the heat transfer effect. The fin heat dissipation mode can be divided into different forms, heat exchangers used on the surface of some heat consumption electronic devices and in the air. Application of this mode can reduce heat sink heat resistance, but also can improve the effect of heat dissipation. For some relatively large power electronic period, it can be used to deal with the turbulence in aviation. By adding a spoiler to the radiator, the effect of heat transfer can be improved by introducing turbulence into the surface flow field of the radiator.
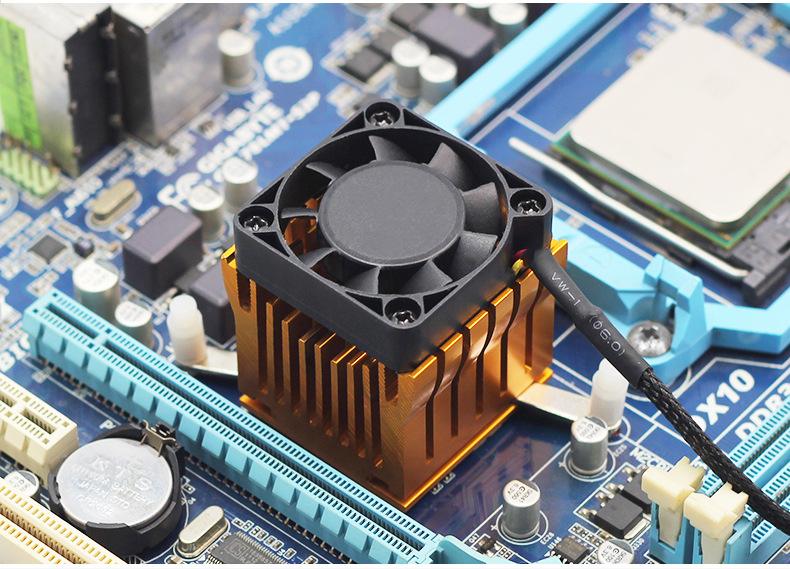

3,Liquid cooling method is a cooling method based on the formation of chip and chip components. Liquid cooling can be divided into direct cooling and indirect cooling. Indirect liquid cooling is the application of liquid coolant and direct contact with electronic components, through the intermediate media system, the use of liquid module, heat conduction module, injection liquid module and liquid substrate and other auxiliary devices in the transmission of the heat element between. Direct liquid cooling method can also be called immersion cooling method, that is, the liquid and related electronic components directly contact, through the coolant to absorb heat and take away heat, mainly in some heat consumption volume density is relatively high or in the high temperature environment of the application of devices.
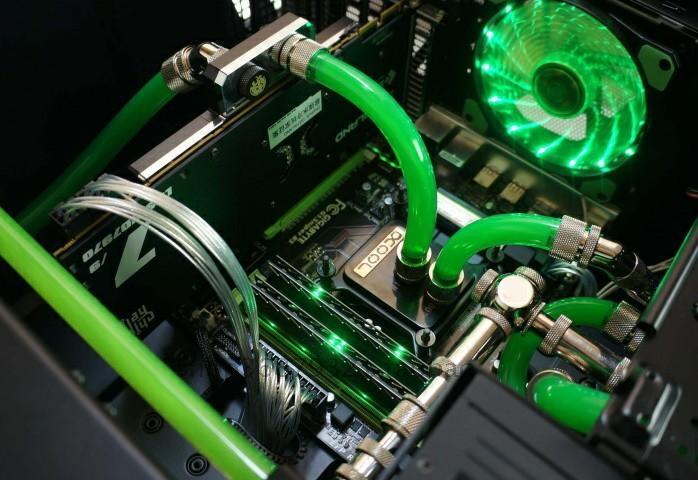

4,The cooling method of cooling or cooling method mainly includes phase change cooling of refrigerant and Pcltier cooling. The way it takes is different in different environments, so it should be applied reasonably based on the actual situation. Phase change cooling of refrigerant is a way to absorb a large amount of heat through the phase change of refrigerant, which can cool electronic devices in some specific situations. The general state is mainly through the refrigerant evaporation to take away the heat in the environment, which mainly includes volume boiling and flow boiling two types. In general, cryogenic technology also has important value and influence in the cooling of electronic components. In some relatively large power computer system can be used in cryogenic technology, not only can improve the cycle efficiency, the number of refrigeration and temperature range is also relatively wide, the structure of the whole machine equipment is relatively compact and the cycle efficiency is relatively high. Pcltier cooling uses semiconductor cooling to dissipate or cool some conventional electronic components. It has the advantages of small size, convenient installation, strong quality, and easy disassembly. This way is also known as thermoelectric refrigeration, through the semiconductor material itself Pcltier effect, in the DC through different semiconductor materials in series under the action of electric couple, can absorb heat at both ends of the couple, release heat, so that the effect of refrigeration can be achieved. This method is a negative thermal resistance of refrigeration technology and means, its stability is relatively high, but because of its relatively high cost, efficiency is relatively low, in some relatively compact volume, and for the cooling requirements of the environment is low. Its heat dissipation temperature ≤100℃; Cooling load ≤300W.
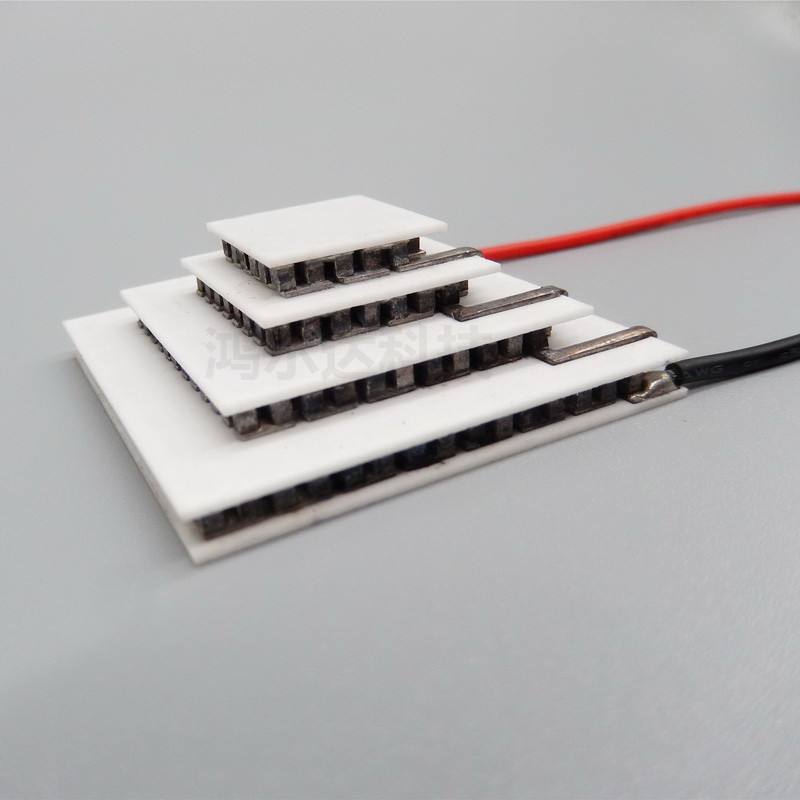
5,The transfer of heat from electronic devices to another environment by means of heat transfer elements. In the process of the integration of electronic circuits, the number of high-power electronic devices increases gradually, and the size of electronic devices becomes smaller and smaller. In this regard, it requires that the heat dissipation device itself should have certain heat dissipation conditions, and the heat dissipation device itself should also have certain heat dissipation conditions. Because the heat pipe technology itself has certain characteristics of thermal conductivity, good isothermal characteristics, has the advantages of heat flux variability, good constant temperature characteristics, and can quickly adapt to the environment in the application, it is widely used in the heat dissipation of electronic and electrical equipment, and can effectively meet the characteristics of flexibility, high efficiency and reliability of the heat dissipation device. At present, it is widely used in the cooling of electrical equipment, electronic components and semiconductor components. Heat pipe is a kind of high efficiency and phase change heat transfer mode, which is widely used in the heat dissipation of electronic components. In practice, the heat pipe must be designed separately for different kinds of requirements, and the influence of gravity and external force and other factors must be analyzed. In the process of heat pipe design, it is necessary to analyze the material, process and cleanliness of the production, to strictly control the quality of the product, and to monitor its temperature.

6,A typical heat pipe consists of a shell, a porous capillary core and a working medium. In the vacuum state, the working medium absorbs the heat generated by the heat source from the evaporation section and vaporizes. Under the action of tiny pressure difference, the working medium flows rapidly to the condensing section and releases latent heat to the cold source to condense into liquid. The condensing liquid then returns to the evaporation section from the condensing section under the action of capillary suction suction of the liquid core, and then absorbs the heat generated by the heat source. This cycle repeats, transferring heat from the evaporation to the condensing. The greatest advantage of heat pipe is that it can transfer a lot of heat under the condition of small temperature difference. Its relative thermal conductivity is hundreds of times that of copper, which is called "near superconducting heat body". However, any heat pipe has a heat transfer limit. Heat pipe has not been widely used in the cooling of power electronic equipment because the technology of micro heat pipe is not mature at present.